
Competition is fierce and user attention spans are dwindling. So, mastering the art of conversion is paramount for any online business. Conversion Rate Optimisation (CRO) has emerged as the cornerstone of digital success, leveraging User Experience (UX) principles to create seamless journeys that guide users towards desired actions. Let’s delve into the intricate synergy between UX and CRO and explore how businesses can optimise their conversion strategies for maximum impact.

Understanding User Experience (UX)
User Experience encompasses the overall experience a user has while interacting with a product or service. It encompasses various elements such as usability, accessibility, design aesthetics, and overall satisfaction. At its core, UX aims to fulfil the user’s needs and expectations in the most efficient and enjoyable manner possible.
UX plays a pivotal role in shaping user behaviours and influencing conversion rates. A well-crafted UX design anticipates user needs, reduces friction points, and guides users seamlessly through the conversion funnel. Elements such as intuitive navigation, clear call-to-action (CTA) buttons, and responsive design are instrumental in enhancing user engagement and driving conversions.

UX-CRO Nexus
User satisfaction and conversion goals may seem like two distinct entities, but they are inherently intertwined. The user experience encompasses every touchpoint a user encounters, from the moment they land on a website to the point of conversion. By prioritising UX principles, businesses can create seamless, intuitive experiences that resonate with users, laying the foundation for successful conversion journeys.
However, optimising user experience alone may not suffice in driving conversions. This is where Conversion Rate Optimisation (CRO) enters the picture. CRO techniques are designed to systematically enhance a website’s performance, maximising the percentage of visitors who complete desired actions. By aligning UX principles with CRO goals, businesses can bridge the gap between user satisfaction and conversion objectives, thereby unlocking the full potential of their digital presence.

Key UX Principles for Conversion Optimisation
Simplify Navigation
Complex navigation structures can overwhelm users and impede their journey towards conversion. Streamlining navigation by organising content hierarchically and implementing intuitive menus enhances usability and keeps users focused on their conversion goals.

Optimise Page Load Speed
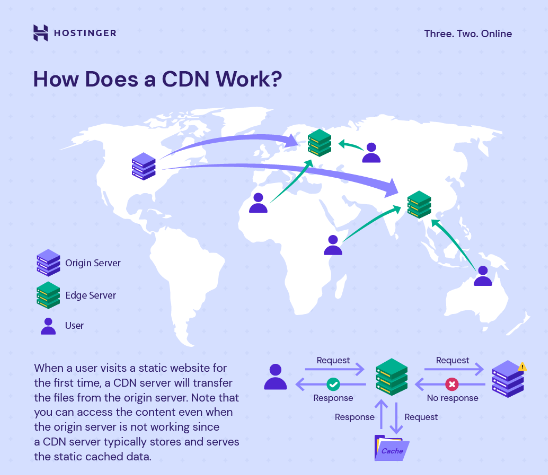
In the digital environment, every second counts. Slow-loading pages not only frustrate users but also adversely impact search engine rankings. Optimising page load speed through techniques such as image compression, minification of CSS and JavaScript files, and leveraging content delivery networks (CDNs) is crucial for reducing bounce rates and improving conversions.
Enhance Mobile Responsiveness
With the exponential rise in mobile usage, ensuring a seamless experience across all devices is non-negotiable. Responsive design principles enable websites to adapt fluidly to various screen sizes and resolutions, optimising the user experience irrespective of the device used. Mobile-friendly interfaces not only improve user satisfaction but also contribute significantly to conversion rates.

Craft Compelling CTAs
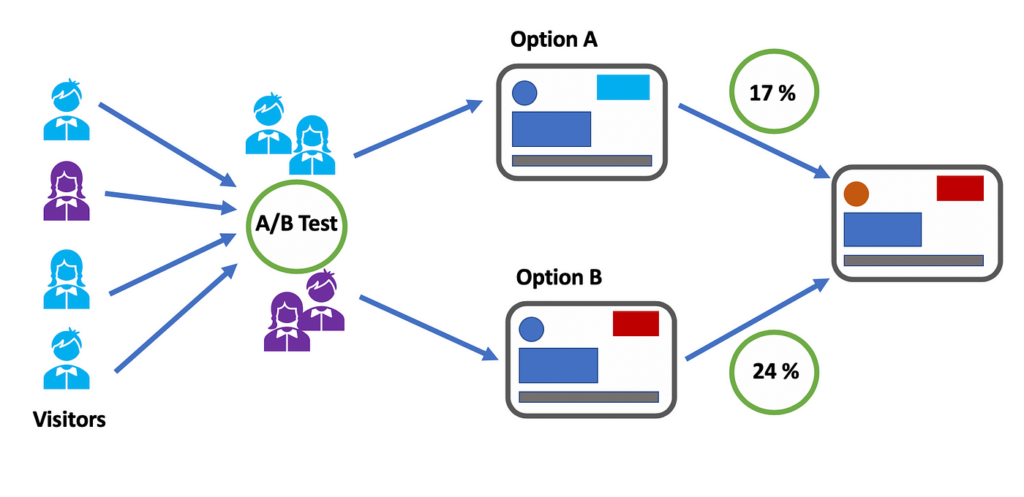
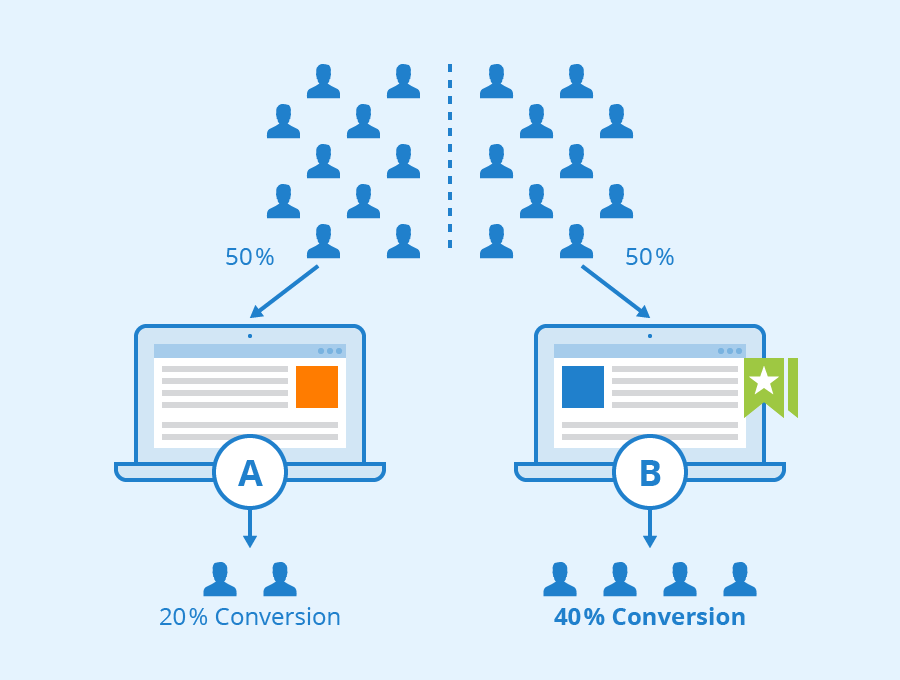
The effectiveness of Call-to-Action buttons cannot be overstated in conversion optimisation. CTAs should be visually prominent, action-oriented, and clearly communicate the desired action. A/B testing different CTA variations enables businesses to identify the most effective wording, colour schemes, and placement for maximum impact.
Optimising User Experience for Conversion: Key UX Strategies
To effectively drive conversions, businesses must implement key UX strategies tailored to optimise the user experience. These strategies encompass various facets of UX design, each playing a crucial role in guiding users seamlessly towards conversion points.
Usability Enhancements
Ensuring ease of use and navigation within a digital interface is paramount. By streamlining user interactions and minimising friction points, businesses can create a more intuitive experience that encourages users to take action.
Accessibility Considerations
Catering to users with diverse needs is imperative for fostering inclusivity and accessibility. Implementing features such as alt text for images, keyboard navigation, and scalable fonts ensures that all users can engage with the website effectively.

Consistency in Design
Maintaining consistency across the interface fosters familiarity and reduces cognitive load. By adhering to consistent design elements such as colour schemes, typography, and interaction patterns, businesses can instil confidence in users and facilitate seamless navigation.

Importance of Feedback and Responsiveness
Providing timely feedback and responsiveness to user actions instils confidence and enhances engagement. Features such as progress indicators, error messages, and real-time updates keep users informed and engaged throughout their journey, ultimately leading to higher conversion rates.

Key Metrics for Evaluating UX-CRO Performance
Effective measurement is the linchpin of success in any digital endeavour. By tracking and analysing key performance metrics, businesses can gain actionable insights into user behaviour, identify areas for improvement, and make data-driven decisions to optimise their strategies. When it comes to UX-CRO initiatives, measurement becomes even more critical, as it allows businesses to gauge the impact of their efforts on both user satisfaction and conversion rates.

Bounce Rate
Bounce rate refers to the percentage of visitors who navigate away from a website after viewing only one page. A high bounce rate may indicate that users are not finding what they’re looking for or that the website lacks engagement. By monitoring bounce rate, businesses can identify potential usability issues or mismatches between user expectations and website content, allowing them to make necessary adjustments to improve user engagement and retention.

Session Duration
Session duration measures the average amount of time users spend on a website during a single visit. A longer session duration generally indicates higher engagement and interest in the content or offerings. By tracking session duration, businesses can assess the effectiveness of their UX design in capturing and retaining user attention, as well as identify opportunities to enhance content relevance and engagement.

Conversion Rates
Conversion rates quantify the percentage of website visitors who complete a desired action, such as making a purchase, signing up for a newsletter, or filling out a contact form. Tracking conversion rates is essential for evaluating the effectiveness of CRO techniques in driving desired outcomes. By analysing conversion rates across different user segments or conversion pathways, businesses can identify areas of friction or opportunities for optimisation and refinement.

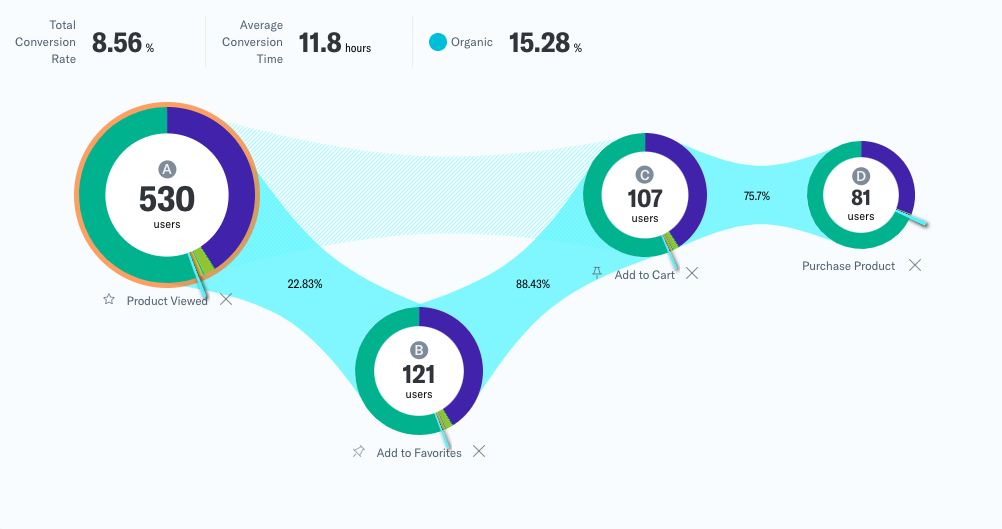
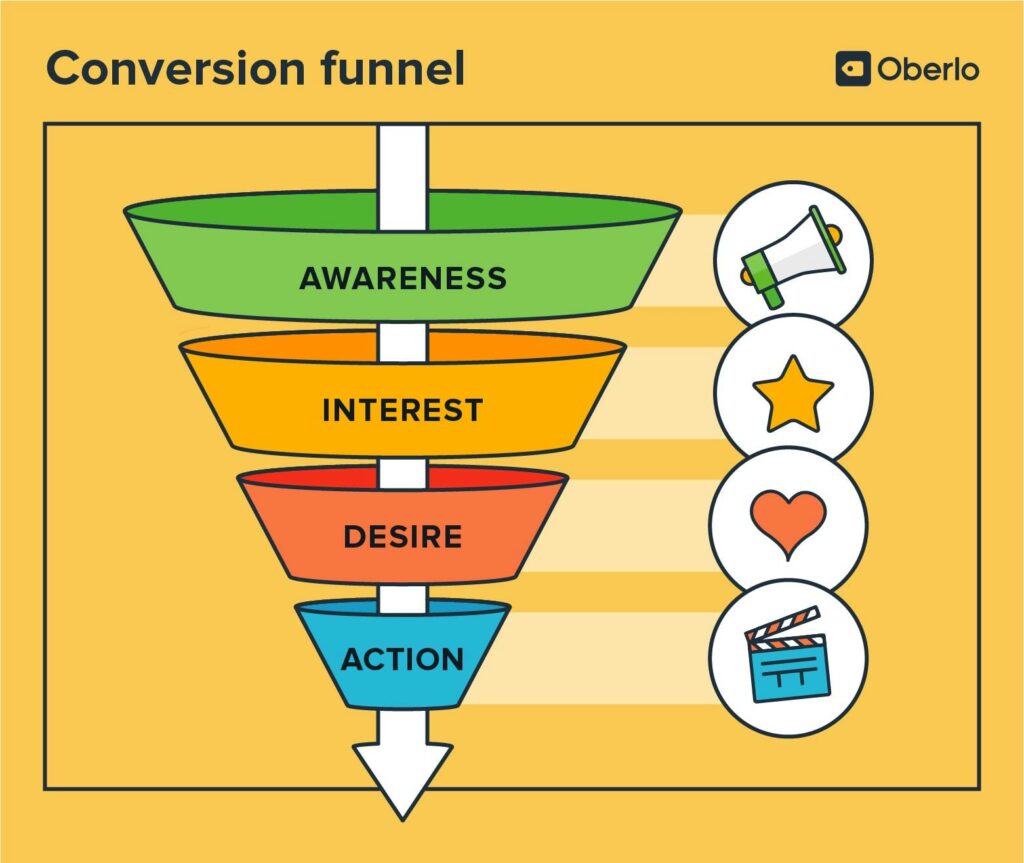
Funnel Analysis
Funnel analysis involves tracking user interactions and behaviours throughout the conversion process, from initial engagement to final conversion. By mapping out conversion funnels and identifying drop-off points or bottlenecks, businesses can pinpoint areas for improvement and optimise the user journey to maximise conversion rates. Funnel analysis provides valuable insights into user behaviour and preferences, allowing businesses to tailor their UX-CRO strategies for optimal performance.
Use of Analytics Tools
Utilising analytics tools such as Google Analytics, Hotjar, or Mixpanel is instrumental in tracking and optimising UX-CRO performance over time. These tools provide valuable data and insights into user behaviour, website performance, and conversion metrics, enabling businesses to make informed decisions to enhance their digital strategies.

The Intersection of UX and CRO
While UX focuses on creating delightful user experiences, CRO is concerned with maximising the conversion potential of those experiences. By integrating UX principles into CRO strategies, businesses can create a synergy that optimises both user satisfaction and conversion rates. A data-driven approach, leveraging analytics tools and user feedback, enables continuous refinement of UX elements to align with evolving user preferences.

User expectations are ever-evolving, mastering the interplay between UX and CRO is imperative for sustainable growth and success. By prioritising user needs, eliminating friction points, and continuously optimising conversion strategies, businesses can create compelling experiences that not only delight users but also drive tangible results. Remember, in the pursuit of conversion, the journey matters as much as the destination, and a seamless user experience is the bridge that connects them both.










































Recent Comments